National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease: a practical approach.
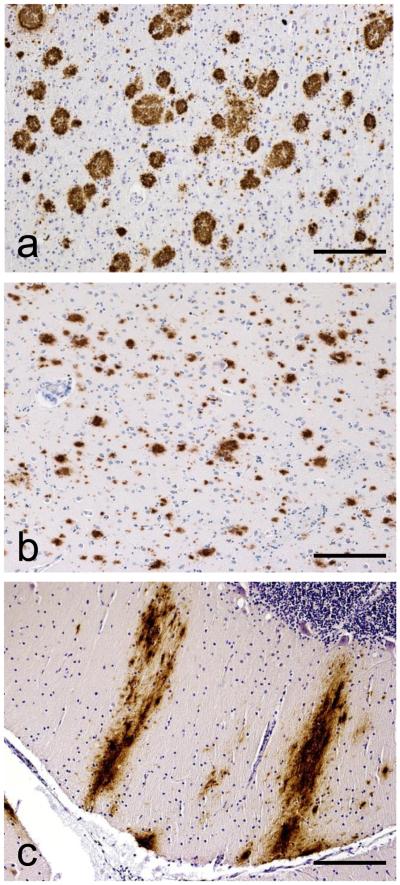
We present a practical info for the implementation of not too way back revised National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s sickness (AD).
Major revisions from earlier consensus requirements are: (1) recognition that AD neuropathologic modifications may occur in the apparent absence of cognitive impairment, (2) an “ABC” ranking for AD neuropathologic change that comes with histopathologic assessments of amyloid β deposits
(A), staging of neurofibrillary tangles
(B), and scoring of neuritic plaques
(C), and (3) further detailed approaches for assessing usually co-morbid circumstances resembling Lewy physique sickness, vascular thoughts hurt, hippocampal sclerosis, and TAR DNA binding protein (TDP)-43 immunoreactive inclusions. Recommendations are additionally made for the minimal sampling of thoughts, hottest staining methods with acceptable choices, reporting of outcomes, and clinico-pathologic correlations.

Research agenda for frailty in older adults: in the direction of a larger understanding of physiology and etiology: summary from the American Geriatrics Society/National Institute on Aging Research Conference on Frailty in Older Adults.
Evolving definitions of frailty, and improved understanding of molecular and physiological declines in a quantity of applications that may improve vulnerability in frail, older adults has impressed investigators from many disciplines to contribute to this rising space of evaluation.
This article experiences on the outcomes of the 2004 American Geriatrics Society/National Institute on Aging conference on a Research Agenda on Frailty in Older Adults, which launched collectively a quite a few group of scientific and first scientists to encourage further investigation on this house. This conference was primarily focused on bodily and physiological aspects of frailty.
Although social and psychological aspects of frailty are critically important and profit future evaluation, these issues had been largely previous the scope of this meeting. Included on this text are sections on the evolving conceptualization and definitions of frailty; physiological underpinnings of frailty, along with the potential contributions of inflammatory, endocrine, skeletal muscle, and neurologic system modifications; potential molecular and genetic contributors; proposed animal fashions; and integrative, system biology approaches that may help to facilitate future frailty evaluation.
In addition, a quantity of explicit recommendations as to future directions had been developed from methods put forth by people, along with recommendations on definition and phenotype enchancment, methodological enchancment to hold out scientific analysis of individual-system and multiple-system vulnerability to stressors, enchancment of animal and cellular fashions, software program of population-based analysis to frailty evaluation, and the enchancment of huge collaborative networks whereby populations and sources may very well be shared. This meeting and subsequent article weren’t meant to be a full consider of frailty evaluation; instead, they’d been and are speculated to current a more-targeted evaluation agenda-setting course of.
