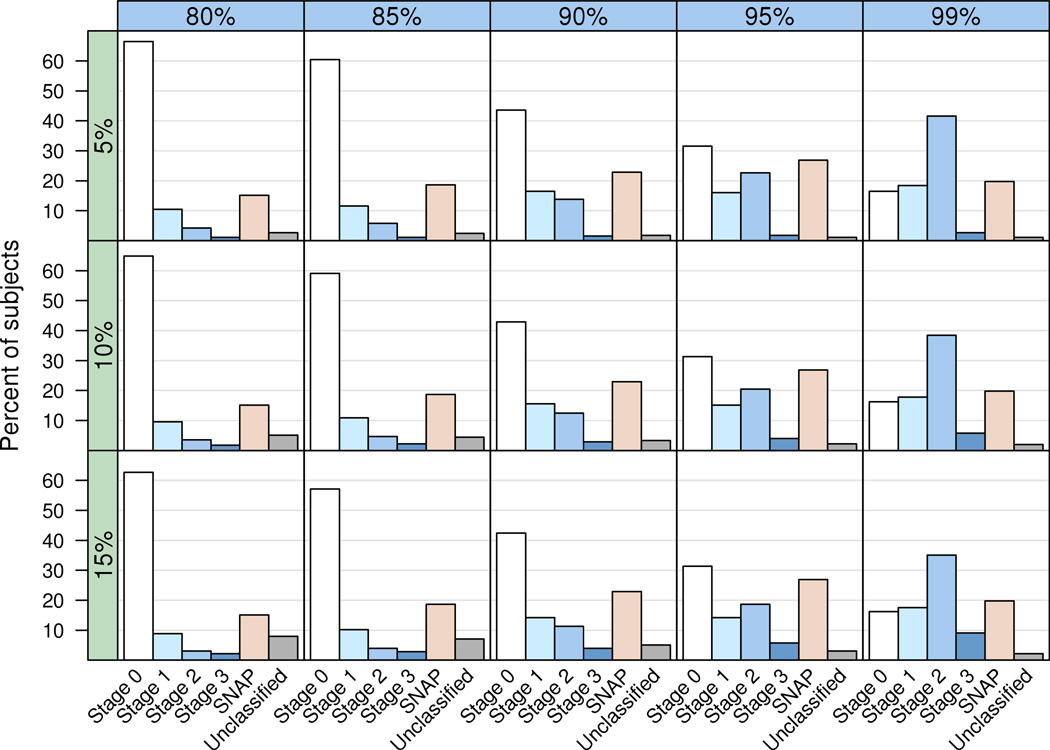
Both endogenous and exogenous sources in alterations of macromolecules like proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids as a result of OS 3. The efficacy of intracellular ROS-scavenging machines precipitates additional mutations and fragmentation of both DNA, and the damage to the adrenal gland and dysregulation at the degrees of cortical transcripts 4. Cellular aging, chronic inflammation, and cancer response from the accumulation of DNA damage over time . Harm to DNA’s effects include defects in DNA methylation, accumulation of mutagenic adducts strand breaks, telomere shortening, and alterations like chromatin reorganization modifications, mutations, and law . OS is largely connected with modifiable lifestyle-related elements like smoking, alcohol intake, pesticide exposure, occupational risks, excessive cell phone use, emotional strain, a sedentary lifestyle, lack of exercise, dysfunctional eating habits, along with frequent intake of depleted junk food . From the adoption of healthy lifestyle alterations, antioxidant supplementation assists in lowering OS levels. The nucleoside type of 8-OHG is 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), that has been suggested as an indicator of oxidative DNA damage in vivo and in vitro 235, 236 8-OHdG additional may be exposed to keto-enol tautomerism to prefer the byproduct 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodG), which can be commonly used as a marker of oxidative DNA damage 237, 238 Several research reported that a direct correlation between 8-OHG formation and carcinogenesis 239 Modified levels of 8-OHG/8-OHdG revealed an association with pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Down’s syndrome, Parkinson’s disease, normal aging, and cancer 237, 240 – 248 For instance, Ames and colleagues have demonstrated the age-dependent accumulation of 8-OHdG at DNA from several rat organs 249 Elevated amounts of 8-OHdG and OH8Gua, yet another markers of oxidative DNA damage, in senescent human diploid fibroblast were revealed 250 DNA adducts derived from dC oxidation, 2′-deoxycytidine (dC)-5-hydroxy-2′-deoxycytidine (OH5dC), 5-hydroxy-2′-deoxyuridine (OH5dU), along with 5,6-dihydroxy-5,6-dihydro-2′-deoxyuridine (dUg), were detected in organs of different aged rats at levels like those of 8-OHdG 251 It might promote spontaneous mutagenesis, resulting in aging and cancer. We’d love to indicate that their research might also have identified confirmed biomarkers for HD, as demonstrated here: institution at the onset of the ailment with genes regulating DNA repair could be represented by the changes we discovered at the item of the DNA excision repair, 8-OHdG; institution with genes regulating plasma association, harm, and fission could be represented by the observed increase in mtDNA from the plasma and the advantage obtained by inhibiting excess mitochondrial fission with P110; and affiliation with enzymes regulating on-reductase action can associate with enhanced aldehydic load, according to protein adduction of 4-HNE, a byproduct of oxidative stress. We discovered that the degrees of these parameters differed between R6/2 HD mice and WT mice. Brain aging is related to a radical imbalance involving antioxidant defenses and intracellular concentration of ROS as illustrated by raises in goods of lipid per-oxidation, protein oxidation, DNA oxidation, oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA and the electron transfer chain, perturbations in mind calcium and iron homeostasis and changes in plasma cysteine homeostasis.rn The overproduction of free radicals may result in oxidative damage to biomolecules, (lipids, proteins, DNA), eventually resulting in numerous chronic diseases such as diabetes, diabetes, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, post-ischemic perfusion trauma, myocardial infarction, cardiovascular diseases, chronic inflammation, stroke and septic shock, aging and other degenerative diseases in humans 27, 93 Excessive NO is cytotoxic by blending with tyrosine which is necessary for catalytic function of receptor ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase or simply by forming ONOOֿ. A research from our lab reported that the progress in sperm DNA integrity by estimation of DNA fragmentation indicator, ROS levels, total antioxidant capacity (TAC), and seminal 8-OHdG degrees at baseline and after 4 months of YBLI 16. A decrease in ROS levels in 10 days of yoga and meditation training was noted together with decrease in improvement and DNA damage in sperm DNA integrity over a span of 6 weeks 28, 11. In our analysis, we’ve found significantly higher rates of ROS, DNA fragmentation index (DFI), and 8-OHdG (de worth < 0.0001 for all the parameters) in fathers of NFSHRb children as compared with fathers of healthy children 48. 8-OHdG, one of the most commonly used indicators of oxidative damage of cells, is a potent mutagenic oxidative DNA base lesion. Repair mechanism (lower OGG1levels) and DNA damage detection (lower PARPlevels) in spermatozoa are inefficient and hence become susceptible to oxidative insults 41. Human spermatozoa are most vulnerable to OS-induced damage as they contain high concentrations of unsaturated fatty acids, possess low levels of cytosolic antioxidant enzymes, cannot undergo apoptosis, can generate ROS via their mitochondria, and possess nuclear DNA that is incompletely protaminated and poorly compacted 31. Lifestyle factors like smoking, alcohol consumption, excessive mobile phone usage, sedentary lifestyle, psychological stress, dysfunctional eating habits, lack of exercise, and pesticide exposure result in high oxidative stress 6. Hence, improvement of lifestyle/social habits becomes necessary for the men seeking to improve their fertility and for their future generations by cessation of smoking, avoidance of excessive alcohol consumption, the adoption of simple lifestyle intervention like yoga and meditation, minimizing the exposure to harmful xenobiotics, and increased dietary uptake of antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables.rnThe vicious cycle of OS and cancer leads to genomic instability due to different alterations like double or single strand DNA breaks, replication errors, foundation alteration, foundation oxidation, along with DNA cross-linking, resulting in cell malfunction, cell death, and DNA mutation 20, 21. Excessive ROS production contributes to the creation of reactive, toxic intermediates along with also the most popular oxidative DNA base adduct, 8-OHdG, that is proven to induce mutations and protect against methylation, acts as the very possible indicator of OS-mediated DNA damage, and is a risk factor for several diseases like cancer 22. 8-OHdG is the most widely studied and is known to cause the vast majority of DNA lesions and is raised in several cancers 23. 8-OHdG also generates dose-related gains in cellular transformation and effective at inducing mutations which are generally found in neoplasia 18, 23, 24. That’s the reason why we estimated that the levels of 8-OHdG for a marker of oxidative DNA damage in its plasma and sperm levels in their offspring. By comparison, there are numerous research based on the evaluation of urinary excretion of 8-OHdG asserting no substantial accumulation of oxidative DNA damage results from several exercise types like repeated bouts of cycling (20), long-distance jogging (28) and swimming (29). In another thorough study correlating sex and lifestyle factors like exercise and diet, the authors detected no substantial differences between classes of both trained and untrained people as soon as protein/lipid/DNA oxidative stress markers such as 8-OHdG were examined (30). In cases like this, HNE responds with surrounding molecules close to the website of its creation, thus boosting chain-reactions of their mitochondria-derived apoptosis again 105 This procedure seems to be involved in cancer and atherosclerosis 106, 107 Therefore, it’s been proven that HNE could cause mitochondria-mediated apoptosis from the pheochromocytoma (PC12) cell line and colorectal carcinoma cells 100, 108 A statistically significant increase in MDA and HNE levels was detected in primary pancreatic cancer, suggesting the institution of esophageal carcinogenesis with severe oxidative stress 109 Immunohistochemical staining of HNE adducts has been shown in animal models of liver cancer 110 HNE therapy of MG63 human osteosarcoma cells may activate caspase-3 and modified the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, thus causing cell death 111 A current study showed that HNE improved the development of breast cancer cells and encouraged their angiogenesis and intrusion 112 Elevated levels of MDA were detected in plasma and blood serum of patients with breast, lung, ovarian, thyroid, and oral cancer, and precancer countries 113 – 122 The MDA levels in patients with lung cancer associated with all the cancer stage 123 Additionally, significantly higher amounts of salivary MDA were determined in squamous cell carcinoma and pre-cancer patients 124. They’re considered markers of their oxidative stress 57 – 61 These products possess unique properties compared to ROS since the non-charged construction of aldehydes permits them to migrate through membranes and cytosol and, therefore, to create far-reaching harmful effects within or outside of the cells 62, 63 There is objective proof that HNE and MDA can alter the amino acid residues and form stable adducts resulting in protein harm 85, 86 Additionally they can form covalent adducts with polyunsaturated fats, and tissue lipids.rnThat is true in particular for cancer cells, which often exhibit high levels of oxidative stress, whereas elevated levels of LPO products exist only in certain cancer types, based on the lipid composition of cellular membranes, the existence of inflammation and the degree of aldehyde metabolizing enzymes 3, 4 However, in inflammatory and neurodegenerative ailments the growth of ROS almost always were accompanied by means of LPO and, as a result, LPO solutions. Disturbances in the normal redox state of cells may cause hazardous effects through the creation of peroxides and free radicals which harm all elements of the mobile, such as proteins, lipids, and DNA preventing pressure from nitric oxide triggers foundation damage, along with strand breaks in DNA Base harm is largely indirect and due to reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated, e.g. O2− (superoxide radical), OH (hydroxyl radical) and H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide). Citation desired Further, several reactive oxidative species behave as mobile messengers in redox signaling.rnAging was associated with increases in the amounts of endogenous ROS and declines in antioxidant defenses, resulting in a vast assortment of cognitive impairment in mobile structures, such as lipid peroxidation of membranes, enzyme inactivation, protein oxidation, and DNA damage 3 – 5 Studies assessing the use of mitochondria in aging have verified that mitochondria aren’t just a supply of cellular energy but also a significant resource for, and goal of, ROS 6, 7 That study has clearly shown that age-associated cognitive damage differs among organs and cell types 8. As covered in this paper, the harm to mitochondria revealed in HD patients and HD mice versions induces oxidative damage to the DNA and may be quantified by the existence of 8-OHdG, a primary marker of hydroxyl radical damage to DNA, in plasma and urine (Shigenaga et al., 1989). But, there are conflicting studies regarding the usage of 8-OHdG as an oxidative stress markers: plasma and urine in R6/2 mice have been found to have elevated levels of 8-OHdG utilizing high-energy liquid chromatography with an electrochemical detection analytical procedure in a research (Bogdanov et al., 1999, 2001). In a careful research on cohorts of both presymptomatic and symptomatic HD patients (32 per ), Borowsky et al. (2013) reported that plasma 8-OHdG wasn’t discovered for a biomarker of disease development when utilizing liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry assay or liquid chromatography-electrochemical variety assay.rnYoga is a mind-body medication, which can help enhance general quality of life by decrease in psychological strain and contains promotive, preventative, curative, and rehabilitative potential 42. The increased risk of childhood disorders could be attributed to reduction of sperm DNA integrity, aberrant methylation patterns (hypomethylation of both oncogenes and hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes), accelerated telomeric attrition, mitochondrial dysfunction, preoxidative harm to the sperm plasma membrane, microsatellite instability, and dysregulation in amounts of mRNAs/transcripts.3 ⇑ ) are explored as potential biomarkers of oxidative/nitrosative strain in certain human diseases (104) (105), such as renal cell carcinoma and diabetes (5) (104). Substantial gains in glutathionylated hemoglobin and glutathionylated actin are discovered in the bloodstream and fibroblasts, respectively, of patients with Friedreich ataxia (106). During significant oxidative stress, e.g., in patients with acute hematologic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis, Lupus erythematosus, chronic lymphedema, or chronic renal failure, serum HNE is raised to speed as much as 3- to 10-fold greater than physiologic concentrations (48). Additionally, HNE could be an important mediator of cognitive stress-induced apoptosis (22), cell regeneration, and signaling pathways (46). HNE is shaped under conditions in concentrations, but its creation is improved in metropolitan conditions. Jinhwan Lim’s research revealed that considerable increases in oxidative damage to DNA, proteins and lipids in ovarian interstitial tissue may be utilized as markers of adrenal changes 28 After ozone inhalation, the ovarian tissue of exposed mice revealed increased expression of oxidative damage markers, such as in 8-OHdG, 4-HNE and NTY. The oxidative stress brought on by AFB1 could possibly be among the underlining mechanisms for AFB1-induced cell injury and DNA damage, which eventually result in tumorigenesis 37 Studies have shown that AFB1 changes cell cycle and apoptosis-signaling pathways in liver mobile versions 43, 47, 51, 52 AFB1 may lead to a rise in ROS formation in animals’ target organs such as rat liver disease, duck liver, and mouse lung 37, 44, 53 it’s suggested that AFB1 induced a significant liver cell injury, as revealed by the substantial growth in nitric oxide, but also a powerful lipid peroxidation in the liver and kidney, followed closely by a substantial reduction in overall antioxidant capacity in rats 53, mice 54, along with poultry 55 Additionally, it had been shown that a powerful inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and nitrotyrosine immunoreactivity were detected in the livers of girls administered by 300 ppb of AF.